Gløsrover

|
A WLAN connected 4WD rover made to cruise the hallways of NTNU Gløshaugen. Those days are over, but the rover remains and keeps its name. |
Mark 1: eBay-frame with aluminum platform
Hardware
Undercarriage:- 4WD plastic robot platform from eBay
- Made out of 2 mm aluminium
- EOSEFF main board
- EOSEFF power supply
- Bread board with LM298N H-bridge
- RC ESC for controlling the LEDs
- 1.3 GHz 1 W Lawmate PAL video transmitter
- Spektrum RC-receiver
- Made of 2 mm aluminium
- HXT900 RC-servo
- KX131 CCD camera
- 2 x 3W warm white LEDs with lens









Mark 2: All aluminium custom made rover and upgraded electronics
Undercarriage:- Made out of 2 mm aluminium
- 4 x planetary gearhead motor (25 mm diameter, 200 rpm, 4mm axle, approx. 7 W each)
- 4 x adapter for attaching 12 mm hexagonal mount RC wheel to a 4 mm axle
- 4 x 80 mm diameter 1/10-scale RC-buggy wheels
- EOSEFF IO-board
- Constant current LED driver with PWM input
- Radiocrafts RC1280HP radio transceiver/modem (868 MHz / 500 mW / 4,8 kbps)
- 10 Hz GPS with MT3329-chipset










Mark 3: Upgrading with WLAN and Raspberry Pi
Base plate:- 100 x 100 mm milled bracket with:
- EOSEFF main board (with 4 x UART, 8 x PWM for RC-servos and/or LED dimming and I2C)
- EOSEFF power supply (3.3 V and 5 V regulators, current and voltage measurement, I2C)
- EOSEFF IO-board (2 x H-bridge, 2 x N-channel FETs, 2 x P-channel FETs, temperature sensor, I2C)
- Constant current LED driver connected to the main board
- 100 x 100 mm milled bracket with:
- Raspberry Pi connected to the I2C-bus
- D-Link DWL-G122 USB WLAN adapter
- 2,4 GHz antenna
- The analog camera is exchanged with a Raspberri Pi camera
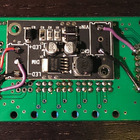
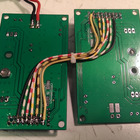
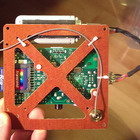




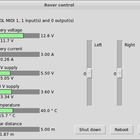
The entire card stack and the Raspberry Pi communicates over I2C. The Raspberry Pi broadcasts telemetry, and a Python-application on the control station picks up the IP, displays the telemetry, and sends back control signals to the rover. A MIDI-controller is used for proportional control over motors, camera/LED tilt and LED dim level. Raw h264 video from the RPi is sent over UDP to the control station with minimum latency (less than 100 ms). In other words, all telemetry, control and video is sent over WLAN, and the 2,4 GHz dipole works very well. In the video below the WLAN access point is actually in another building behind three concrete walls.